Why is deleting duplicate rows necessary?
Setting up Data
The following query will be used.
CREATE TABLE Employee (id int(50) primary key, name varchar(80), salary int(50));
Now, Insert some data into this table. I have inserted some data as below. Have included some famous names for some excitement :p Hope you guys like cricket! We are using the same table we used in finding the Nth highest salary article. But, we will add a few duplicates. The updated table looks something like this :
As you can see, it is clearly visible we have duplicate records, as the ID is the primary key and usually has business logic of auto-increment, we can safely ignore it here.
SQL DELETE using GROUP BY and HAVING clause
The SQL GROUP BY clause is used in this approach to find duplicate entries. The COUNT function may be used to examine the occurrence of a row using the Group By clause, which organizes data according to the provided columns.
For example, if we run the following query, we'll obtain all of the records in the Employee database that have an incidence larger than one.
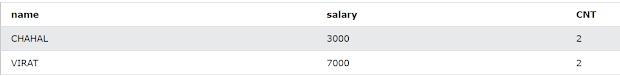
SELECT name, salary, COUNT(*) AS CNT FROM Employee GROUP BY name, salary HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
The result of the following query is as shown below :
We need to preserve only one row and get rid of the duplicates. Only duplicate rows in the table need to be removed. The Emp Virat and Chahal occur twice in the table, for example. We simply want to get rid of one instance of it.
To compute the maximum id of each data row, we utilize the SQL MAX function.
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE id NOT IN ( SELECT MAX(id) FROM Employee GROUP BY name, salary );
The result of the above query is something like below :
We can see that the Select line above leaves out the maximum ID value for each duplicate row, leaving only the minimum ID value.
Replace the first Select with the SQL delete statement as shown in the following query to eliminate this data.
DELETE FROM Employee WHERE id NOT IN ( SELECT MAX(id) FROM Employee GROUP BY name, salary );
Perform a select on an Employee table after executing the delete statement, and you'll obtain the following entries that don't have any duplicate rows.
2. SQL DELETE using RANK function
The PARTITION BY clause is used with the RANK function in the following query. The PARTITION BY clause divides the data into subsets for the provided columns and assigns a rating to each partition.
DELETE E FROM Employee E JOIN ( SELECT *, RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY name, salary ORDER BY id) rank FROM Employee ) T ON E.ID = T.ID;
The results we would get are similar to the previous one. All the duplicates would be removed. The method is a bit more complex than the previous one as you can see but provides a better way to rank the columns and check. You can replace the DELETE keyword with SELECT and by selecting the appropriate columns, you would be able to see the ranks of the columns and the output.
Conclusion
That's all about how to delete or remove duplicate rows from a table in SQL. In this post, we looked at 2 ways to delete duplicate rows in SQL using a variety of methods, including SQL functions. You are free to utilize whatever way makes you feel most at ease. However, I would advise against immediately implementing these techniques and packaging on production data. You should do your tests in a less demanding environment.
- Difference between UNION and UNION ALL in SQL
- 10 Examples of ALTER command in SQL
- MySQL vs NoSQL comparison
- 4 Examples of CASE expression in SQL Server
- How to create and rollback transaction in database?
- Difference between Self and Equi join in SQL
- What are T-SQL Window Functions?
- How to use Stored Procedure in SQL?
- How to convert String to Date in SQL?
- How to use WHERE and HAVING clause in SQL
- How to find top 10 Records in SQL
- Difference between Truncate, Drop, and Delete in SQL



No comments:
Post a Comment